What is Multi-Factor Authentication
Published on 05 Mar 2021
· Around 10 minutes to read
What is Multi-Factor Authentication
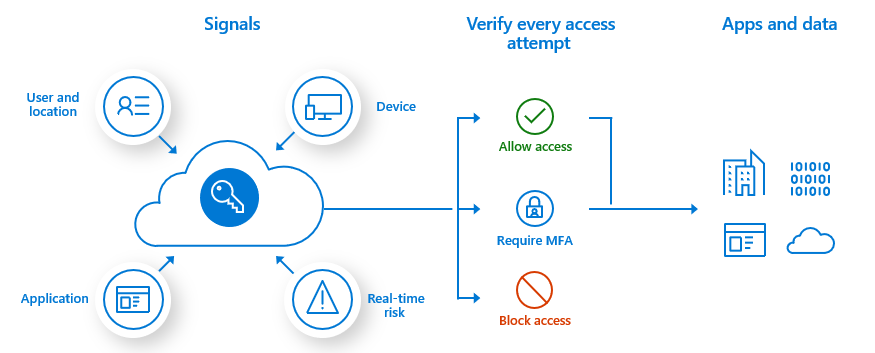
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is a system that increases account security by adding an extra security step when a user wants to access their account, requiring at least two or more types of authentication to prove the user identity.
Why is It Used?
Whenever a user wants to access a user account on any platform, the user basically uses a combination of password and username. However, users may be at a greater risk of password compromise than they assume, especially if they use the same password on multiple websites. If the user's password is compromised, guessed or phished on a system containing sensitive information that does not support the multi-factor authentication mechanism, the bad user who has the password can easily access, manipulate or delete sensitive information. Even downloading simple software or clicking links in emails can expose the user to password theft. The problem encountered is undesirable and can sometimes cause irreversible problems.
But with a multi-factor authentication mechanism, even if the password is compromised by a wrong user, they will need a second factor, making the stolen password useless by itself.
Differences Between Multi-Factor Authentication and Two-Factor Authentication
When MFA is mentioned, 2FA comes to mind. It is even confused by many. MFA and 2FA basically perform the same operations. Both systems increase account security by adding a security step. But there are differences. MFA requires at least two or more types of authentication, while 2FA requires only two types of authentication. We can call 2FA, a subset of MFA.
MFA Mechanisms Used in MonoSign
-
Monosign Mobile Authenticator
MonoSign Mobile Authenticator is a mobile application developed by MonoFor, Inc.
How Does It Work?
When the user wants to log in to a system, it sends an instant message to the user's mobile device and asks the user to prove whether the user is the right person. If the user clicks the confirm button when a notification is received on his mobile device, the user successfully logs into the system. If the user thinks that the login was not done by him / her, he / she can cancel the login process by clicking the reject button. The MoNosign Mobile Authentication application also generates a 6-digit code every 30 seconds. Fingerprint or face recognition, which can only be owned by the user, can also be added to the MonoSign mobile authenticator application. If the user wishes, he / she can log into the system using the renewed code on the mobile authenticator application while logging into the system.
-
Third Party Mobile Authenticators (MonoTP, Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator ... )
Third Party Mobile Authenticators are authenticators developed by other organisations.
How does it work?
Third-party mobile authenticators work like the MonoSign mobile authenticator app. Third-party authenticators also generate a 6-digit code every 30 seconds. The user uses the 6-digit code while logging into the system and the verification process is completed.
-
Text Message (SMS)
When a user wants to log in to the system, they send an SMS to the phone number registered in the system belonging to the user. The user uses the 6-digit code sent via SMS while logging into the system and the verification process is completed.
-
Phone Call
When a user wants to log in to the system, they make a phone call to the phone number registered in the system belonging to the user. The user performs the verification process by applying the step specified in the phone call and logs into the system.
-
Security Key
The physical Security Key is a mini device that works with your USB port. It allows you to securely perform a secondary verification. Anyone who does not have this security key will not be able to access the user account or act on behalf of the user.
-
Personal E-Mail
The personal email verification feature sends a verification code to the second email address the user trusts. Since this code will only be sent to an email address that the user trusts, those who do not have access to this email address will not be able to log into the user account.
MFA Definitions and Uses in MonoSign
MFA Definitions
If no MFA definition has been made on MonoSign before, users can login to the system with their user information.

After logging into the system, clicking on the user picture on the top right, click on the "My Account" tab from the menu that appears.
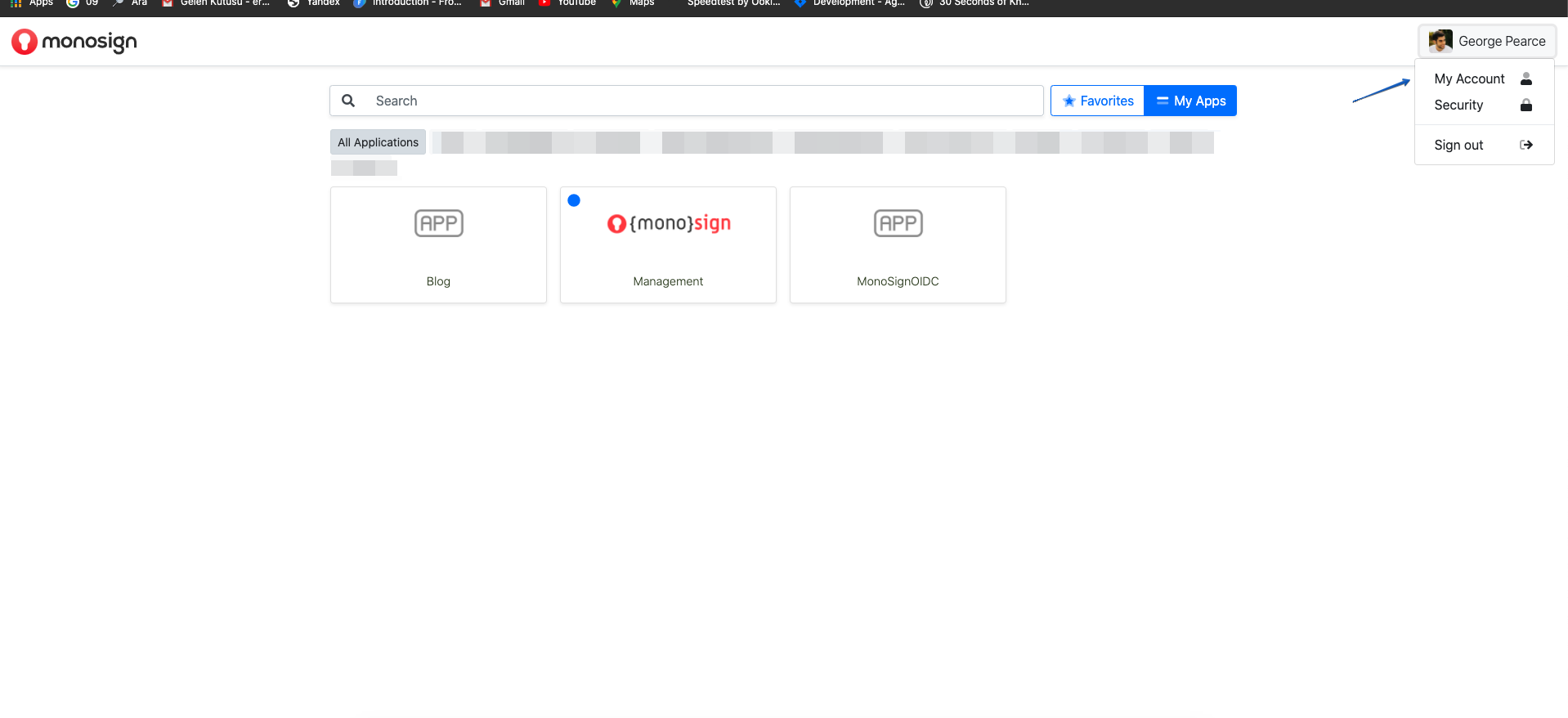
Click on the "Multi-Factor Security" section on the directed screen and click on the "Activate" section at the top right since MFA is not activated at all, and the MFA definition will be made on MonoSign for the user
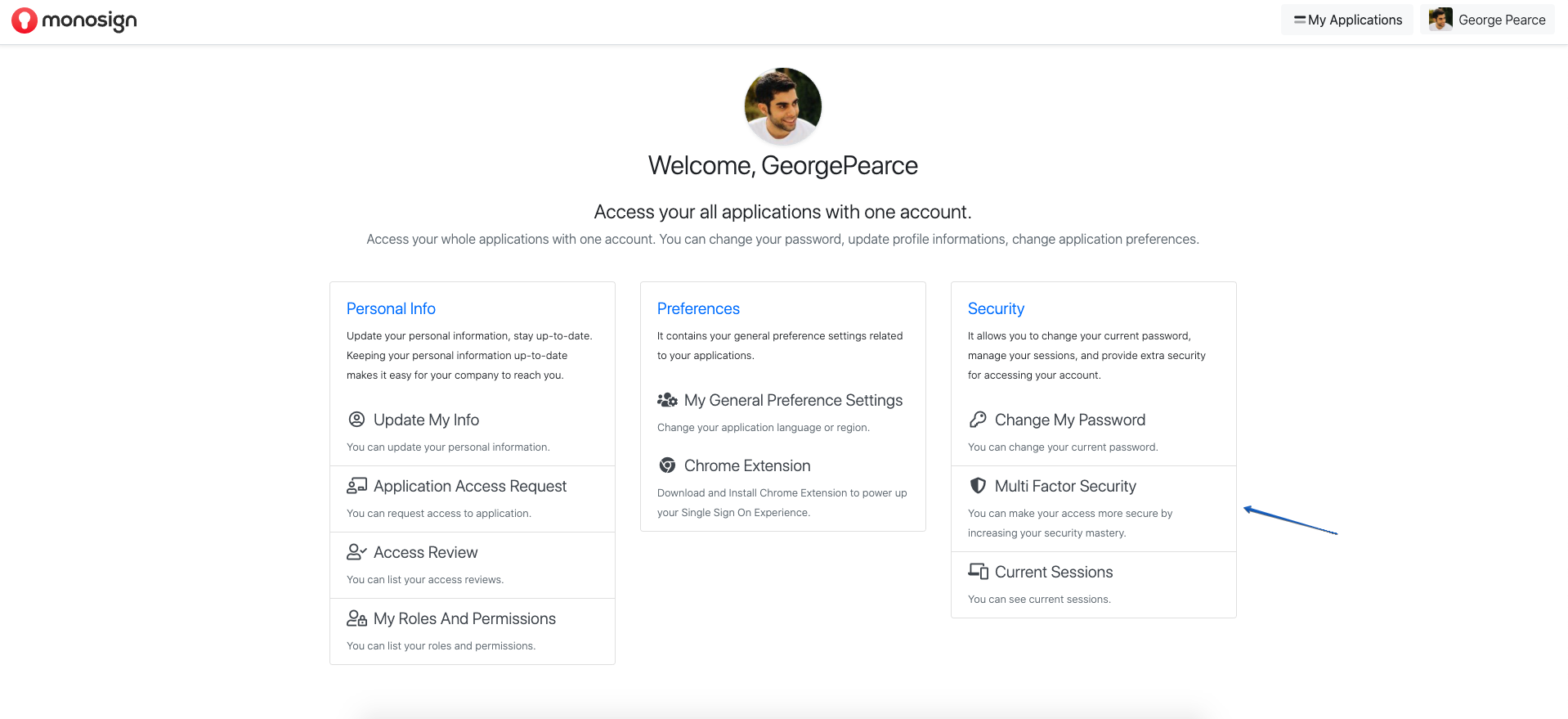
After the MFA is activated, click on the "Use" section to use the Mobile Authenticator.
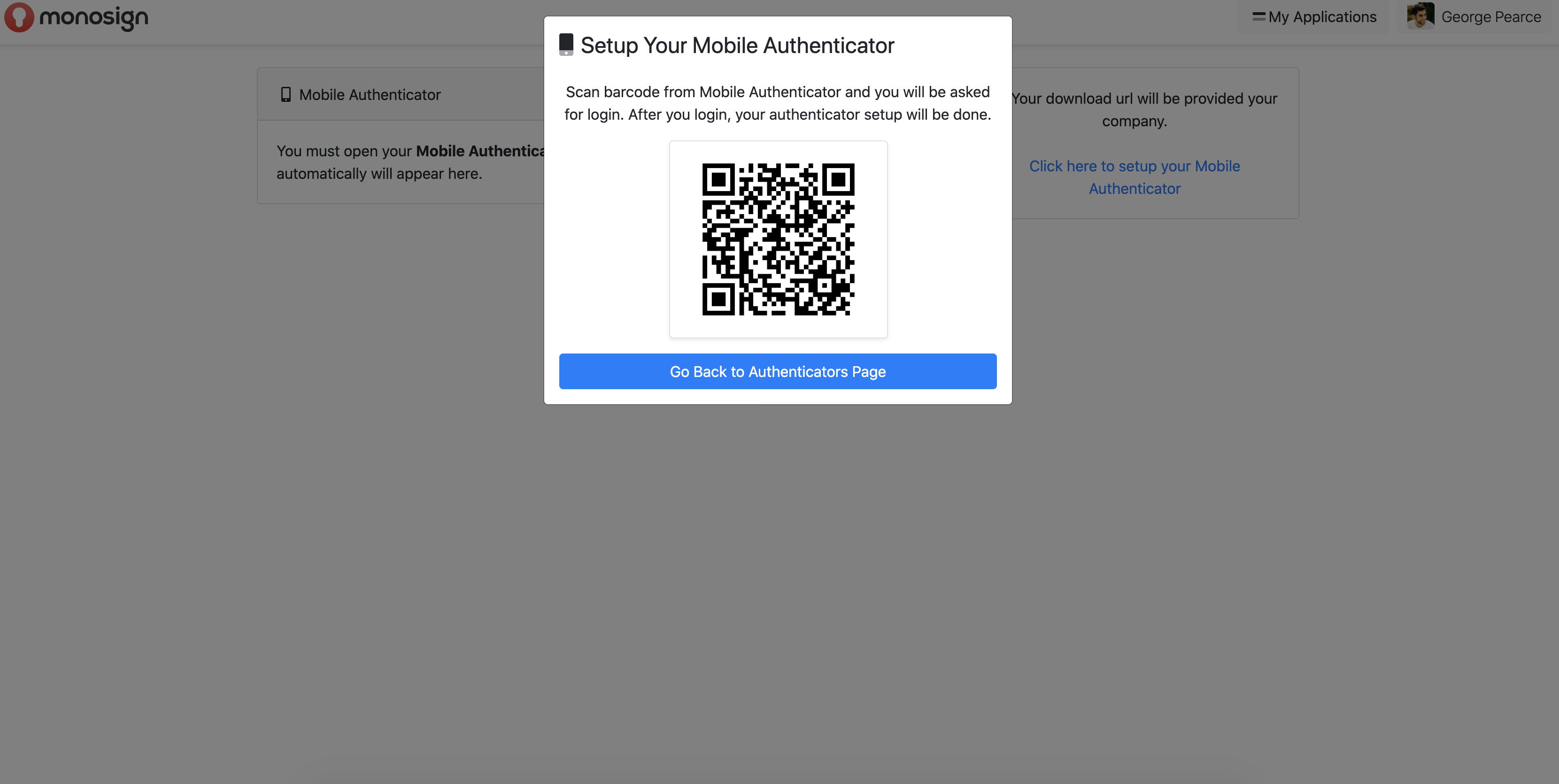
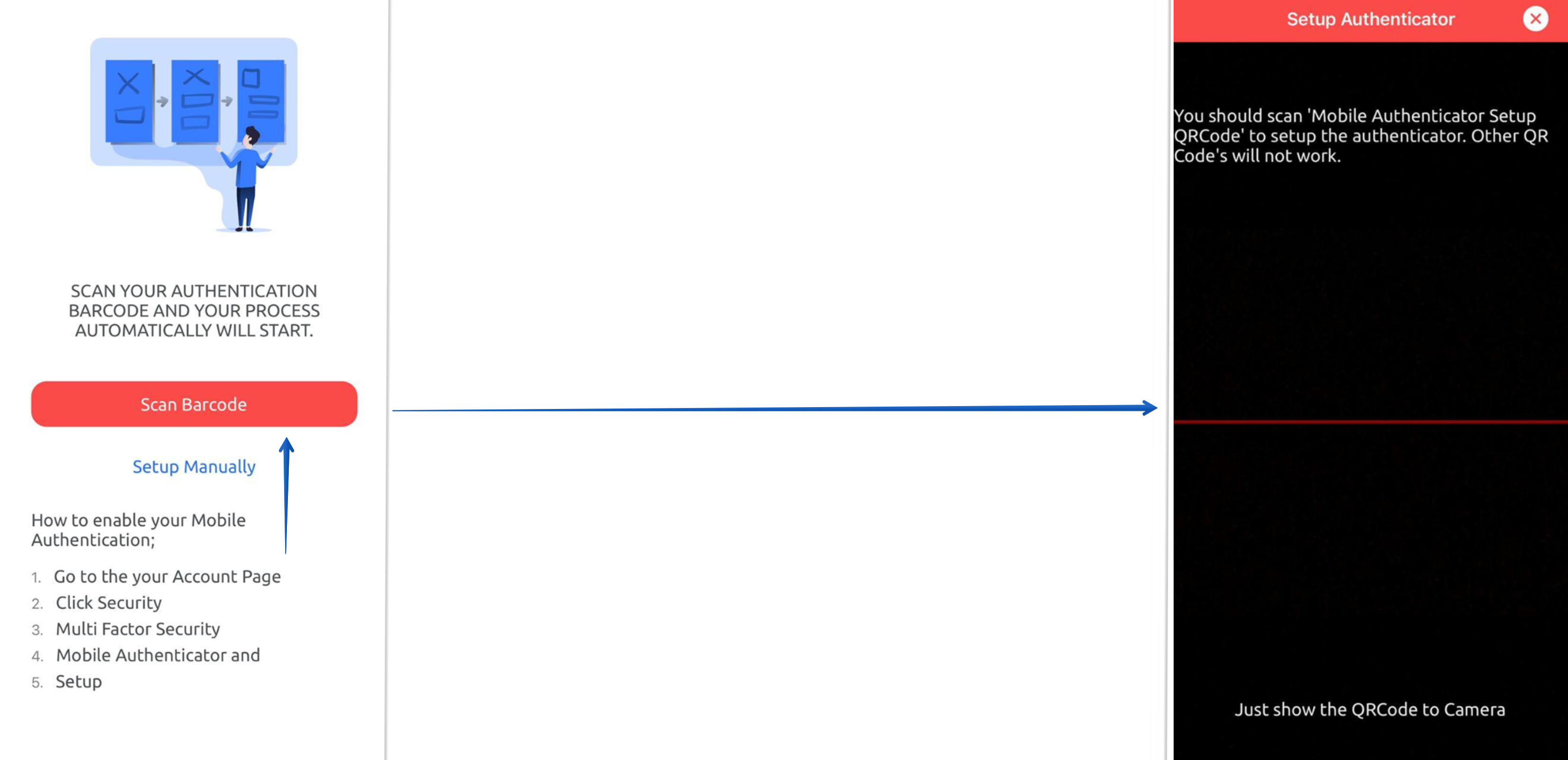
A QR code appears in front of the user, which must be read from the mobile application. The Monosign Mobile MFA application downloaded to the mobile device is entered and the "Scan Barcode" section is clicked. The QR code in the MonoSign application opened on the website is scanned from the QR code reading screen that appears in front of the user, and Mobile Authentication is defined to the user's account.

When the user is directed back to the Multi-Factor Authentication page, it will display that the Mobile Authentication mechanism is active.
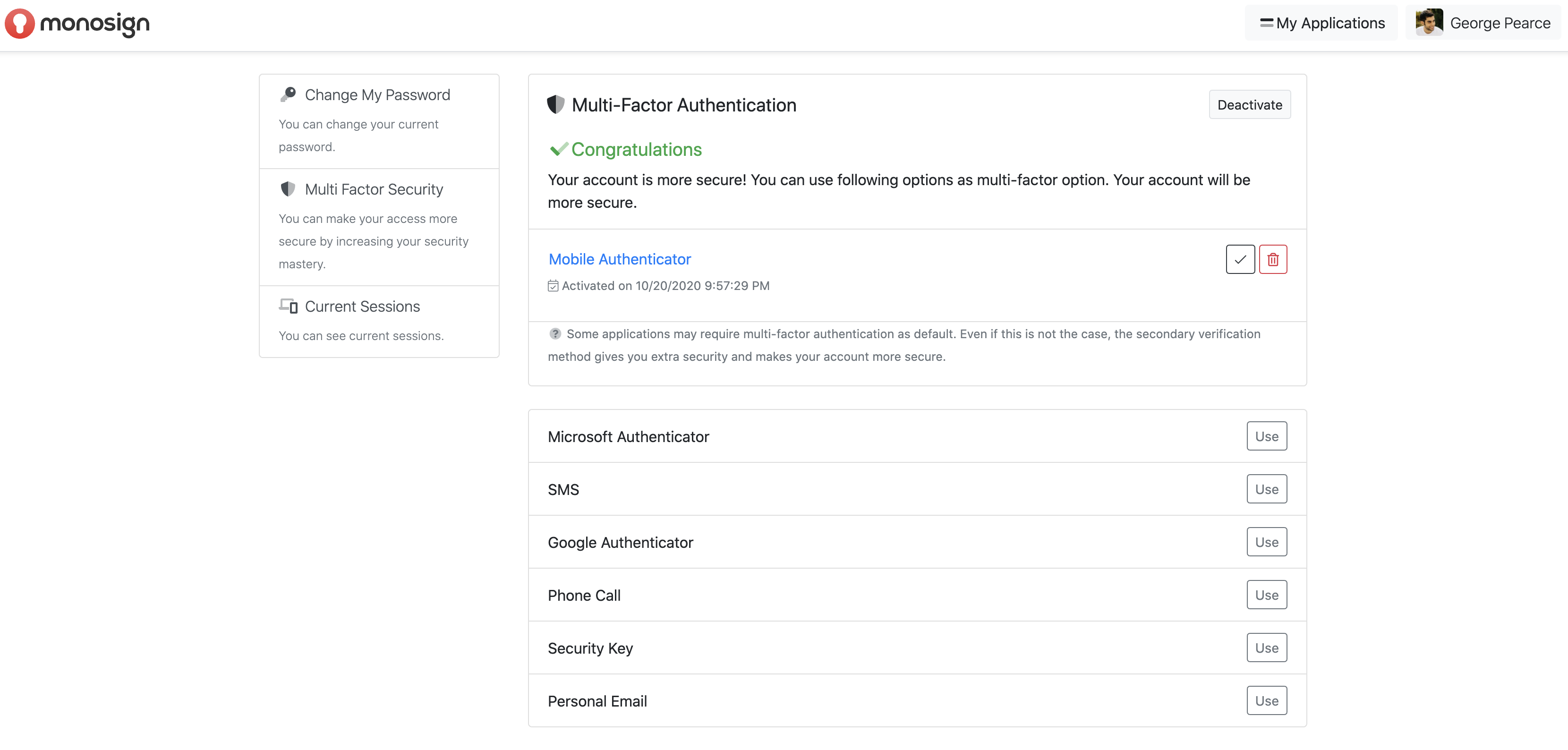
If the user wishes, they can define other MFA mechanisms to the system in the same way.
MFA Usage Areas
If the MFA definition has been made on MonoSign before, the system is entered with user information. After logging in, the security step screen will appear in front of the user.
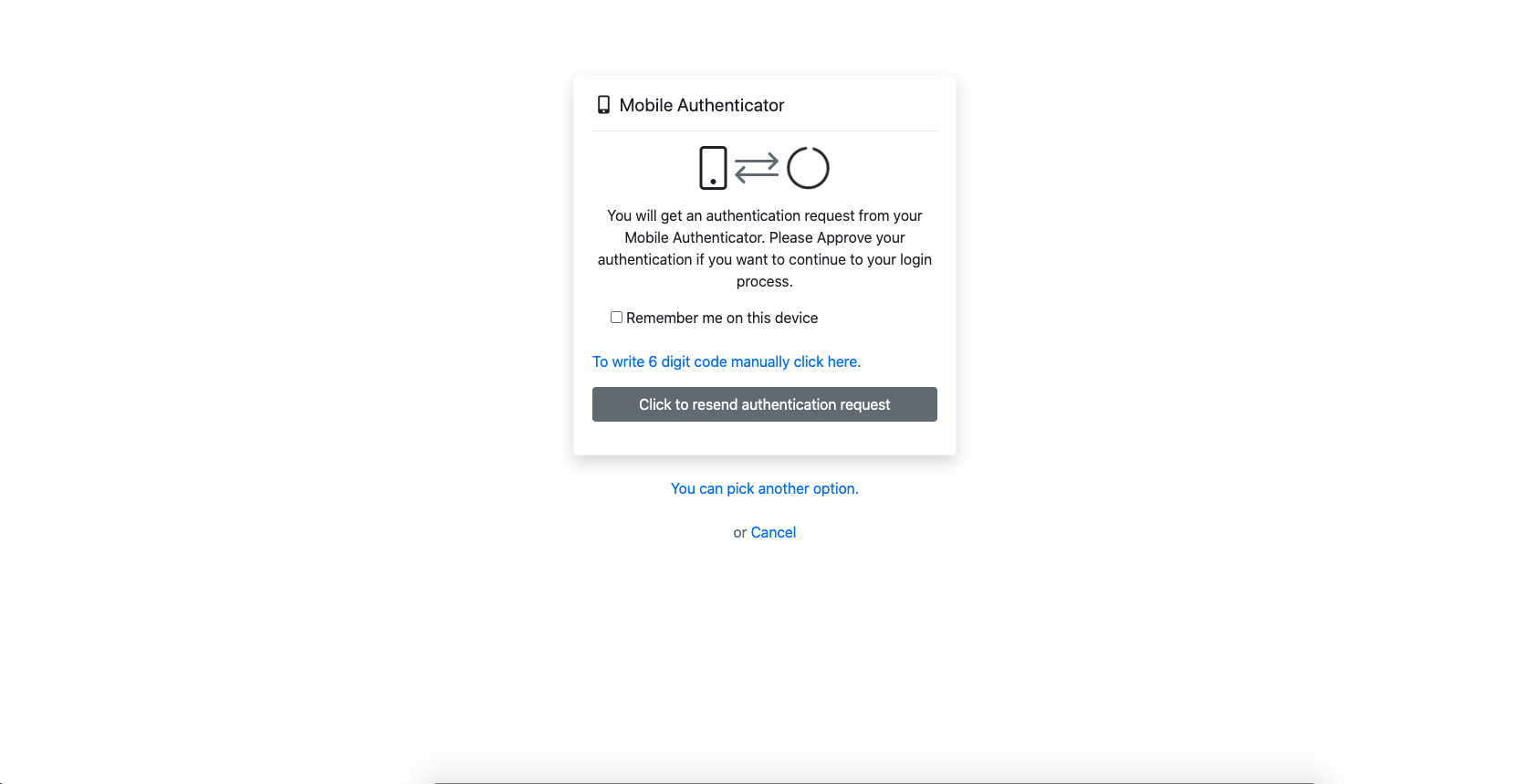
When the user comes across this screen, they receive a notification from the mobile authenticator application. The user may or may not approve the login to the account by holding down the incoming notification. If the user wishes, by clicking the notification, they can direct to the application and perform the approval process from within the application.

If the user has a problem with receiving notifications while trying to log in to his account (if the device settings are not authorized to send a notification for the application etc.), the user clicks "To write 6 digit codes manually click here" when the security step screen appears after the user is logged in. By logging into the verification application on his mobile device, they can perform the verification process by entering the 6-digit code, which is renewed every 30 seconds.
In addition, if the application has a user-specific pin or face recognition or fingerprint reading on mobile devices, it can be defined in the mobile authentication application. Whenever the user wants to log into the application, he / she can log into the mobile application using any of these features.

MFA Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
-
Security:
The primary benefit of multi-factor authentication is that it provides security by adding additional protection to layers. The more factors are available, the lower the risk of the attacker accessing critical systems and data.
-
Compliance and Legal Risks:
In addition to data encryption, state and federal governments have required certain businesses to apply multi-factor authentication to standard operating procedures at the end-user level.
-
Easier Login Process:
Many unregulated businesses resist MFA practices, fearing a more complex login process for employees and customers. However, this extra layer of security allows organizations to redefine and redesign their login processes towards enhanced security.
-
Identifying Security Expectations:
Identifying security requirements and expectations in your organization is an essential part of any MFA implementation. For example, your industry, your business model, applicable compliance regulations (if applicable), and the type of data you capture, use and store to run normal business operations are important considerations. An MFA implementation is an opportunity to define and classify common business scenarios for each organization based on risk level and determine when an MFA session is required.
Disadvantages
-
Blocked Access:
Access to a specific application or system cannot be granted if you do not have access to one of the multi-factor authentication methods and you have not set up backup sources to verify user access.
-
Cost:
Traditionally, MFA can be costly if an organization uses a solution that requires on-premises hardware and must be integrated with existing identity solutions.
-
Login Time:
The time required to log in to your system and verify using a mobile device may increase the login time.